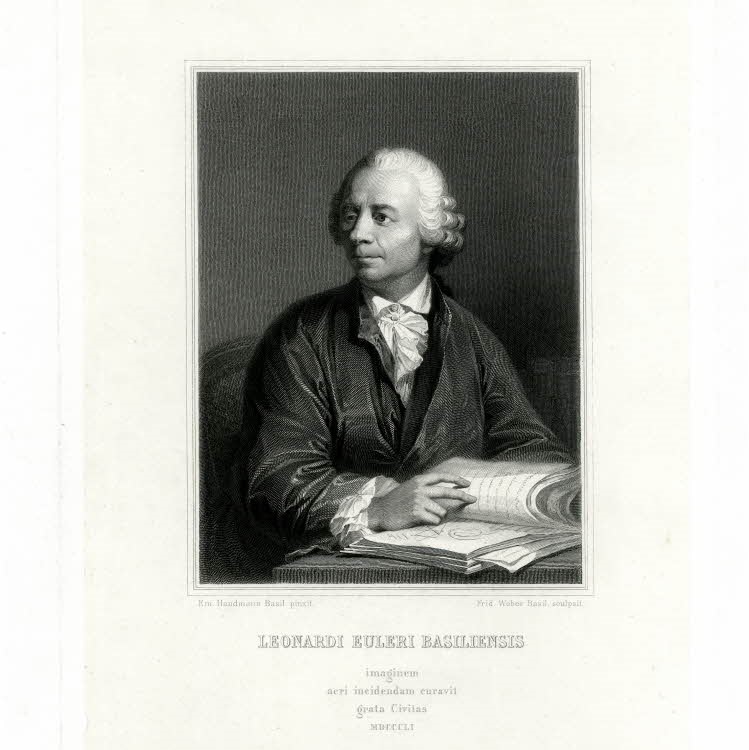
Leonhard Euler
A Tribute Page
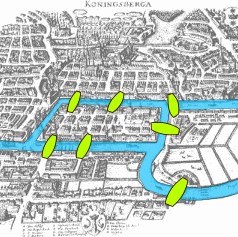
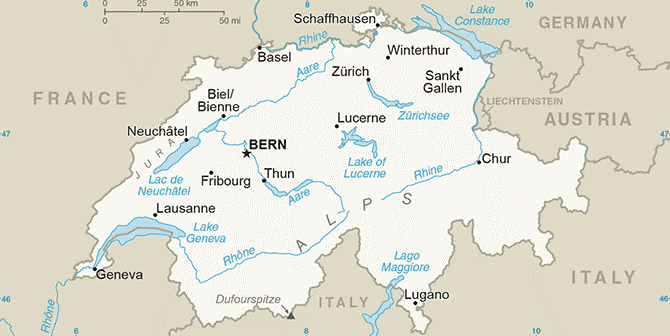
One of the greatest mathematicians of the 18th century, and by many regarded as the greatest thinker of all time. Euler contributed greatly to mathematics as we know it today by further developing techniques in calculus, number theory and differential equations, among other things. For a delightful introduction to Euler and his work, watch A Tribute to Euler a lecture by Euler-expert William Dunham.

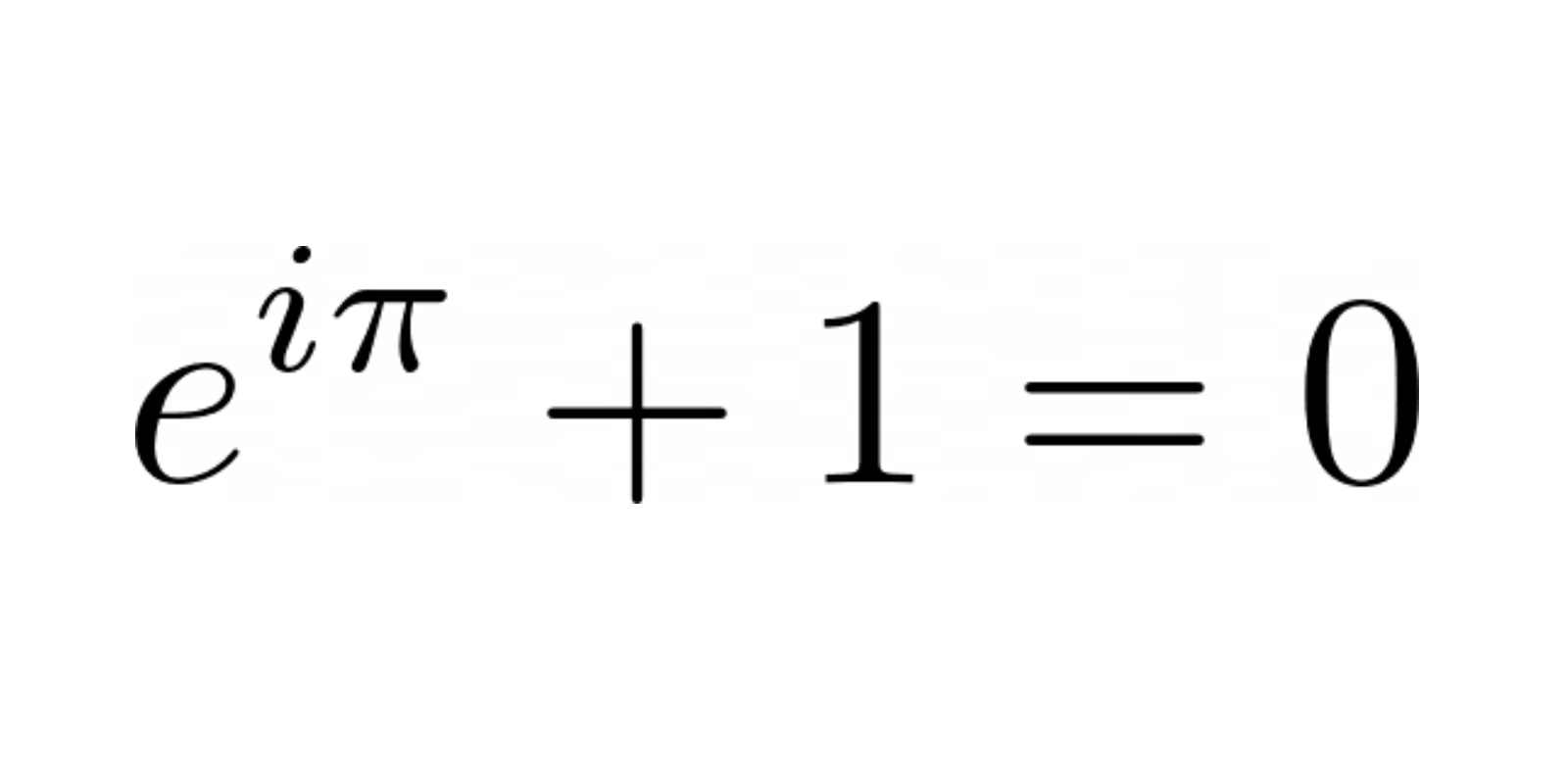

92 volumes published